Ex vivo images of preserved maculas provide a record of tissue appearance prior to destructive histological processing 1. Eyes were preserved by immersion in fixative within 4 hours of death. The best images were obtained from eyes photographed within 24 hours of tissue recovery, from specimens were attached retinas, and from specimens from donors >70 yr.
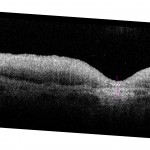
Color: After removal of the leave, globes were fixed by immersion for 24 to 48 hours in 0.1 M phosphate-buffered 1% paraformaldehyde and 2.5% glutaraldehyde or 4% paraformaldehyde. Preserved globes were examined internally after removal of superior and inferior calottes, anterior segment, and vitreous. A horizontal belt of sclera containing the macula, optic nerve was stabilized in a 5-ml polystyrene cup and submerged in 0.1 M phosphate buffer to reduce specular reflections. We used a stereomicroscope with a side-port for stereo photography (SMZ-U; Nikon, Melville, NY). We illuminated specimens in front of the retina with a fiber optic ring light (epi-illumination), a dark-field base that allowed oblique lighting through the sclera (trans-illumination). Both light sources used halogen bulbs at full power. Image were centered on the fovea and sized to emulate Field 1 of the Airlie House classification of diabetic retinopathy grading system 2. Eyes accessioned prior to 2005 were photographed as stereo pairs on 35-mm film (Ektachrome EPJ320T; Eastman Kodak, Rochester, NY). Film was scanned at 1200 dpi. Eyes accessioned after 2005 were photographed as stereo pairs with a digital camera (Nikon, CoolPix) using a ruby bead in the field for an internal scale 3. Eyes accessioned after 2011 were photographed additionally with flash for true color rendition. Files are named SingleID-AgeSex-lighting.jpg, e.g., 0097002L-71M-EE.jpg, where is EE is a lighting field. Lighting could be a single illumination type, such as EE for epi, or a 2-illumination combo, such as ET (epi, trans), or FE (flash, epi). Optical coherence tomography (OCT): A Spectralis® HRA+OCT (software version 5.1.4, Heidelberg Engineering) with a broadband super-luminescent diode at λ = 870 nm as a low coherence light source was used for ex vivo OCT. Full thickness eye wall punches centered on the fovea were excised with an 8.25 mm diameter trephine (Surgistar #310825, Knoxville TN). Tissue was held in a closed, fluid-filled chamber with a +60D lens mounted in one vertical side (from Heidelberg). Some macular punches were sutured at 4 points through the sclera (7-0 curved Vicryl, Ethicon, Somerville NJ) to an anodized aluminum plate with a circular opening that accommodated scleral curvature and the optic nerve. Other punches were held in place within the circular plate by pressure fit only, i.e., without sutures. The plate was held vertically in a slot within the chamber, so that the vitreal surface of the excised macula faced into the Spectralis. We performed horizontal scans through the fovea and optic nerve and volume renditions including 30° slices 60 µm apart. Optical depth resolution was ~7 µm with digital resolution reaching 3.5 µm, per manufacturer. Signal strength at 28-30 db provided the lowest background noise. Ten B-scans were averaged for each image. Resulting images were exported in TIFF (16-bit, 2560×1636 pixels).- Curcio CA, Medeiros NE, Millican CL: The Alabama age-related macular degeneration grading system for donor eyes, Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998, 39:1085-1096
- Group Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group: Report 7. A modification of the Airlie House classification of diabetic retinopathy, Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1981, 21:210-226
- Olsen TW, Feng X: The Minnesota Grading System of eye bank eyes for age-related macular degeneration, Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004, 45:4484-4490